Introduction to Magnetic Resistance in Mechanical Watches
The Growing Threat of Magnetism
Modern lifestyles surround us with magnetic fields. Smartphones produce 5–50 gauss at close range, laptop speakers up to 200 gauss, handbag clasps 500–1,000 gauss, and MRI scanners over 10,000 gauss. Fields exceeding 60 gauss magnetize traditional steel components, leading to rate gains/losses of 10–300 seconds per day or complete stoppage until demagnetized.

Importance of Anti-Magnetic Design
Anti-magnetic mechanical watches deliver reliable precision in magnetized settings. Contemporary models resist 15,000–100,000 gauss with minimal deviation, serving professionals in medicine, engineering, and aviation. These designs preserve mechanical artistry while surpassing quartz in challenging environments.
How Magnetism Affects Mechanical Movements
Interaction with Ferromagnetic Components
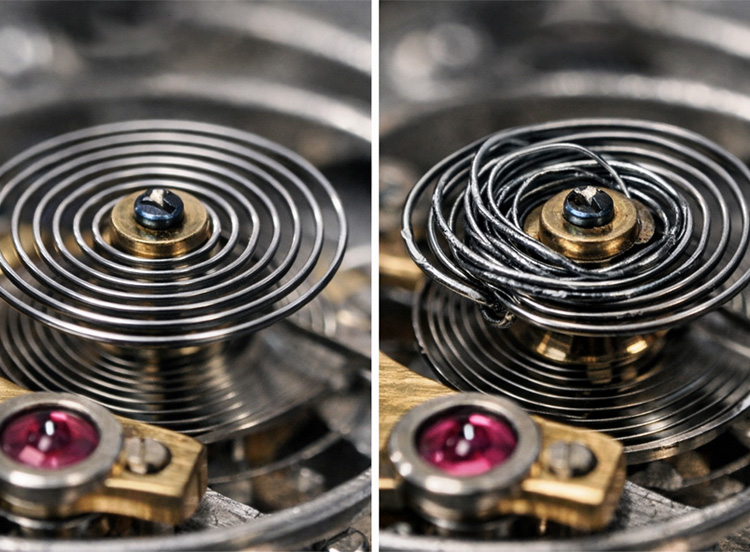
Magnetic fields induce magnetism in ferromagnetic parts like Nivarox hairsprings, steel escape wheels, and pallet forks. This causes the hairspring coils to stick or deform irregularly, disrupting oscillation isochronism and amplitude. Resulting errors range from subtle drifts to dramatic gains/losses until professional demagnetization.
Common Sources and Field Strengths
Everyday exposure varies widely:
| Source | Field Strength (Gauss) | Risk to Traditional Watches |
|---|---|---|
| Smartphone (close) | 5–50 | Low–Moderate |
| Handbag clasp | 100–500 | Moderate–High |
| Laptop/DC speaker | 200–1,000 | High |
| Airport security | 500–2,000 | Very High |
| MRI machine | 10,000+ | Extreme (avoid) |
Traditional movements fail above ~60 gauss; modern anti-magnetic designs withstand 15,000+.
Historical Development of Anti-Magnetic Technology
Early Soft Iron Cages (1930s–1950s)
IWC’s 1948 Mark XI for pilots and Rolex’s 1956 Milgauss (“mille gauss”) employed soft iron inner cages as Faraday shields. These redirect flux lines around the movement, protecting up to 1,000 gauss. The Milgauss featured a soft iron dial and cage, with its lightning-bolt second hand as signature.
Material Advancements (1960s–1990s)
Manufacturers introduced paramagnetic alloys like Glucydur balances and niobium-zirconium springs (e.g., Rolex Parachrom precursor). These raised baseline resistance to ~500–1,000 gauss in tool and scientific watches.
Modern Anti-Magnetic Innovations
Silicon Balance Springs and Escapements
Silicon components are inherently non-magnetic, lightweight (1/3 steel), and corrosion-resistant. Omega’s Si14 springs in Co-Axial escapements (since 2008) and Rolex’s blue Parachrom springs resist >15,000 gauss while improving thermal compensation and shock tolerance.
Advanced Shielding and Hybrid Approaches
Hybrid systems combine soft iron cages with titanium cases and silicon escapements. IWC Ingenieur models achieve 40,000–80,000 gauss resistance through multi-layer shielding and ceramic bearings.
Non-Metallic and Composite Movements
Avant-garde designs like Ulysse Nardin Freak use full silicon or carbon composite escapements, virtually eliminating magnetic vulnerability in high-complication pieces.
Standards and Certification
ISO 764 and METAS Master Chronometer
ISO 764 mandates functionality after ~60 gauss exposure. METAS (independent lab) tests at 15,000 gauss over multiple positions and days, requiring 0–+5 sec/day precision alongside water resistance and power reserve checks.

Manufacturer-Specific Benchmarks
Rolex internally validates Milgauss to 1,000 gauss flux density; Omega’s Aqua Terra >15,000 gauss models undergo METAS protocols with public transparency.
Testing and Real-World Performance
Laboratory Magnetic Exposure Tests
Labs use Helmholtz coils for uniform fields, monitoring timing before, during, and after exposure. Demagnetization via alternating fields restores affected watches.
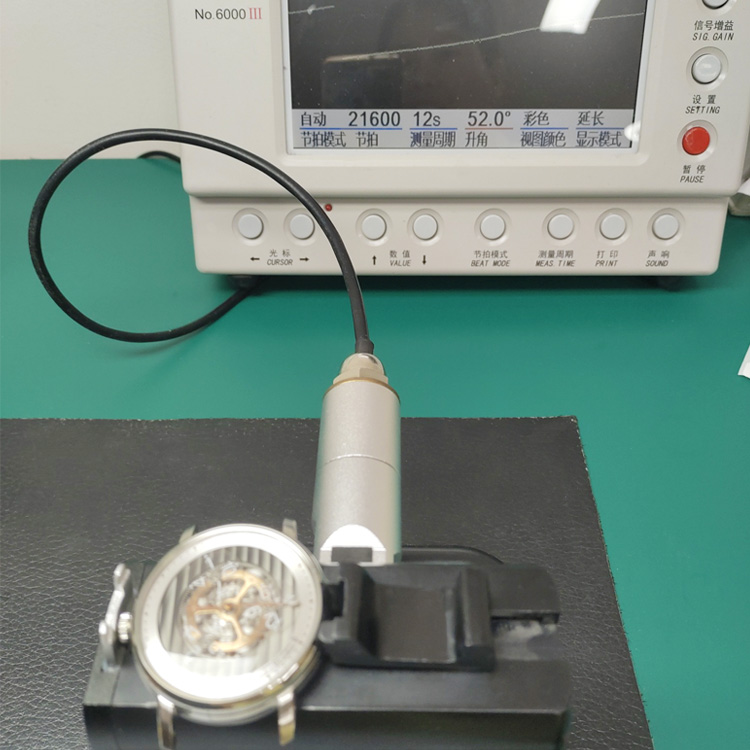

Practical Considerations for Users
Avoid prolonged contact with strong magnets. Compact demagnetizers (available for ~$20) quickly restore legacy watches; modern anti-magnetic models rarely need intervention.
Conclusion: The Future of Anti-Magnetic Mechanical Watches
Integration with Broader Resilience Trends
Anti-magnetic advancements integrate with lubrication-free silicon escapements, extended power reserves (100+ hours), and enhanced shock protection, creating ultra-reliable movements for contemporary demands.
Benefits for Collectors and Daily Wearers
Superior magnetic resistance guarantees unwavering accuracy amid ubiquitous fields, positioning mechanical watches as practical, heirloom-grade alternatives to electronic timepieces in professional and everyday scenarios.





