Time and the Evolution of Timekeeping
Daniel J. Bufenstine once said, “Man’s first and greatest discovery is time.”
Time is one of the most fundamental physical quantities, and modern science now measures it with extraordinary accuracy.
Throughout history, humans have searched for reliable periodic motion to measure time. By dividing repeating cycles into equal parts, people defined the basic unit of time—the second.
Shadows, flowing sand, dripping water, and celestial movement all became early indicators of time’s passage. Over time, humans transformed these natural phenomena into mechanical motion. Clocks then became faithful recorders of human activity, marking seconds, minutes, hours, days, months, and years. This innovation freed humanity from complete dependence on natural cycles.
(Source: https://watcheshome.com/)
Understanding Time
Time has neither a visible beginning nor an observable end. We often represent it as a straight line that flows continuously forward. Time never reverses direction. It moves steadily from the past, through the present, and into the future. Humans measure time using clocks. These instruments allow us to quantify change and compare moments with precision.
Methods of Time Measurement
There are two primary ways to measure time.
1. Measuring a Moment in Time
Moment-based measurement identifies a specific point on the time scale. This method requires both a unit of measurement and a reference point. Midnight serves as the universal starting reference. For example, a train departure at 17:30 uses “hours” and “minutes” as its units.
2. Measuring a Time Interval
Interval measurement calculates the duration between two moments. It requires units but no fixed starting point. For instance, a high-speed train traveling from Beijing to Guangzhou may take eight hours. The unit is “hour,” regardless of when the journey begins.
Establishing Time Standards
In ancient societies, people relied on celestial motion to define time. Daily life followed the rhythm of sunrise and sunset. Just as measuring length requires a ruler, measuring time requires a stable reference.
(Source: https://watcheshome.com/)
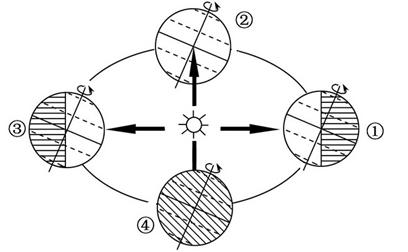
The True Solar Day
A true solar day is the interval between two consecutive solar noons. However, Earth’s orbital speed varies throughout the year. As a result, the length of each true solar day changes. The difference between the longest and shortest true solar days can reach several minutes. This variability makes the true solar day unsuitable as a precise time standard.
The Mean Solar Day
Ancient Egyptians divided a day into 24 hours, each hour into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds. In 1820, French scientists defined the mean solar day by averaging Earth’s rotation over an entire year. This approach established a stable benchmark. One mean solar day equals exactly 86,400 seconds. The scientific community widely adopted this standard for time measurement.
The Almanac Second
In 1939, British scientist Harold Spencer Jones discovered long-term variations in Earth’s rotation. His findings showed that the mean solar day was not perfectly stable. In response, scientists proposed a new benchmark based on Earth’s revolution around the sun. They selected the tropical year measured at noon on January 1, 1900, as the reference. After extensive research, scientists defined one almanac second as 1 / 31,556,925.9747 of a tropical year. This standard officially took effect in 1960 and significantly improved accuracy.
The Atomic Second
The Birth of Atomic Time
Advances in physics revealed that atoms vibrate at exceptionally stable frequencies. This discovery transformed timekeeping. In 1967, the 13th International Conference on Weights and Measures adopted the atomic second, replacing astronomical definitions entirely.
Defining the Atomic Second
Scientists now define one second as 9,192,631,770 oscillations of radiation emitted during a specific energy transition of a Cesium-133 atom. Atomic clocks achieve remarkable precision. They deviate by less than one second over millions of years.
A New Era of Precision
The atomic second officially took effect at 00:00 UTC on January 1, 1972. Since then, time measurement has operated independently of celestial motion. National metrology laboratories now maintain time standards worldwide, ensuring global consistency.
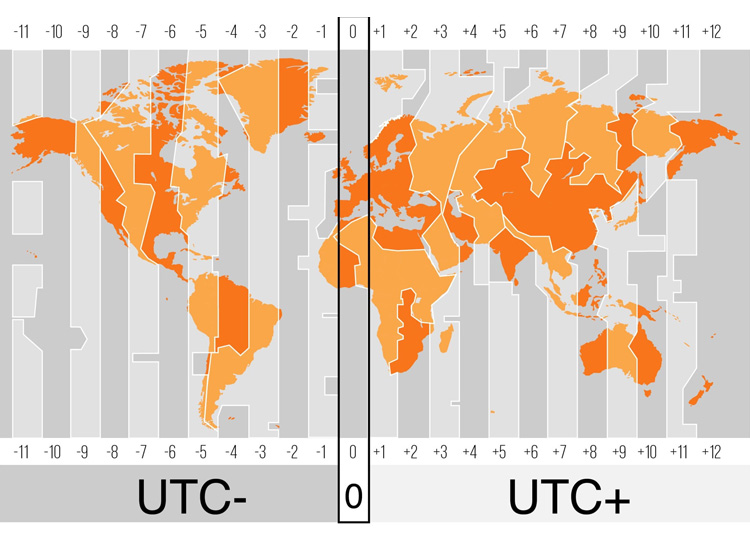
The Global Zone Time System
Before standardized time zones, each city followed its own local solar time, leading to widespread confusion. For example, in 1880, some railway stations displayed multiple clocks showing times for different cities.
In 1879, Canadian railway engineer Sir Sandford Fleming proposed dividing the Earth into 24 time zones. Just four years later, in 1883, the United States adopted four standard time zones. One year after that, the 1884 International Meridian Conference extended the system worldwide.
(Source: https://watcheshome.com/)
The Zero Time Zone
The prime meridian passes through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. The zero time zone extends 7°30′ east and west of this meridian, covering 15 degrees of longitude. From this reference, time zones progress eastward and westward. The eastern and western 12th zones meet near the 180° meridian, which forms the International Date Line.
How the Zone Time System Works
The Earth rotates 360 degrees in 24 hours. Each time zone therefore spans 15 degrees of longitude. Adjacent zones differ by exactly one hour. This system reduced hundreds of local times to just 24 standard times and has supported global coordination for over a century.
niversal Time and the International Date Line
Universal Time, also known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), uses the prime meridian as its reference. To resolve date discrepancies, international organizations established the International Date Line near the 180° meridian. The line avoids land areas whenever possible.
Date Change Rules
-
Crossing the Date Line from west to east subtracts one day.
-
Crossing from east to west adds one day.
These rules ensure global consistency.
The Leap Second
Scientists introduced the leap second in 1972 to keep atomic time aligned with Earth’s rotation. International authorities may add or remove one second at the end of June or December. The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) announces these adjustments. Leap seconds affect scientific systems but remain unnoticeable in daily life.
World Clocks
World clocks apply the zone time system mechanically. A rotating 24-hour ring completes one full rotation while the hour hand completes two.
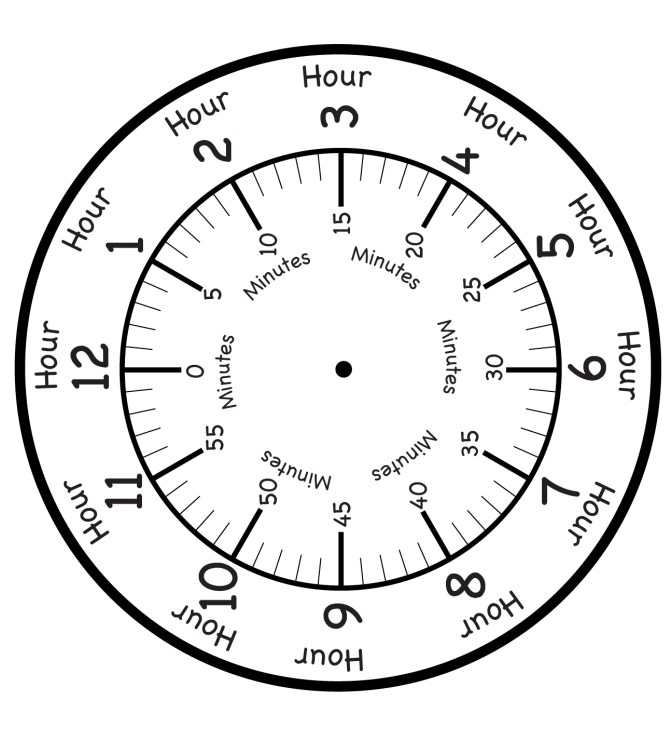
The outer city ring displays major cities across time zones. By aligning the city ring with the 24-hour scale, users can read global time instantly.
(Source: https://watcheshome.com/)